Physical Human Robot Interaction: The aim of this research is to study about novel control algorithms to control robot in human environment. This interaction can be either intentional or accidental. The main idea is to estimate external interactions (without using torque sensor information) and to increase the compliance of the system relying on fast control loops. The estimated interaction is further used to derive the robot appropriately. The algorithms are mainly implemented on KUKA LWR4 and iiwa robot arm.
:People
- Dr. Mehdi Keshmiri, Professor, Robotics, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan
- Dr. Hamid Sadeghian, Assistant Professor, Robotics and control, University of Isfahan, Isfahan
- Dr. Abbas Karami, PhD, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan
:Videos
- https://youtu.be/yI0Gkh4Okpw
- https://youtu.be/ER-Mu98gjLU
- https://youtu.be/wDrH-nhsXos
- https://youtu.be/GZN1LTMHp68
:Related Publications
- Abbas Karami, Hamid Sadeghian, Mehdi Keshmiri, Giuseppe Oriolo, “Force, Orientation and Position Control in Redundant Manipulators in Prioritized Scheme with Null space Compliance,” Control Engineering Practice, 85, pp.23-33, 2019.
- Abbas Karami, Hamid Sadeghian, Mehdi Keshmiri, Giuseppe Oriolo, “Hierarchical Tracking Task Control in Redundant Manipulators with Compliance Control in the Null-Space ,” Mechatronics, pp. 1-14, 2018.
- Abbas Karami, Hamid Sadeghian, Mehdi Keshmiri, “Novel approaches to control multiple tasks in redundant manipulators: stability analysis and performance evaluation,” Advanced Robotics, 32(10), pp. 535-546, 2018.
- Fabio Ruggiero, Janathan Cacace, Hamid Sadeghian, and Vincenzo Lippiello, “Passivity-based control of VToL UAVs with a momentum-based estimator of external wrench and unmodeled dynamics,” Journal of Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 72, pp.139-151, 2015.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Luigi Villani, Mehdi Keshmiri, and Bruno Siciliano, “Task Space Control of Robot Manipulators with Null-Space Compliance”, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 30(2), pp. 493-506, 2014.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Luigi Villani, Mehdi Keshmiri, and Bruno Siciliano, “Dynamic Multi-Priority Control in Redundant Robotic Systems”, Robotica, 31(7), pp. 1155-1167, 2013.
- Fabio Ruggiero, Janathan Cacace, Hamid Sadeghian, Vincenzo Lippiello, "Impedance Control Of VTOL UAVS With A Momentum-Based External Generalized Forces Estimator", IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, 2014.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Mehdi Keshmiri, Luigi Villani, and Bruno Siciliano, “Null-Space Impedance Control with Disturbance Observer”, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS2012, Algarve, Portugal.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Fanny Ficuciello, and Luigi Villani, “Global Impedance Control of Dual-Arm Cooperative Redundant Manipulators”, 10th IFAC Symposium on Robot Control, SYROCO2012, Dubrovnik, Croatia.
- Luigi Villani, Hamid Sadeghian, and Bruno Siciliano, “Null-Space Impedance Control for Physical Human Robot Interaction”, 19th CISM-IFtomm Symposium of Robot design, dynamics and control, ROMANSY19, 2012, Paris.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Mehdi Keshmiri, Luigi Villani, and Bruno Siciliano, “Priority Oriented Adaptive Control Of Kinematically Redundant Manipulators”, International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA2012, Minnesota, USA.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Luigi Villani, Mehdi Keshmiri, and Bruno Siciliano, “Multi-Priority Control in Redundant Robotic Systems”, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS2011, San Francisco, USA.


- Constrained Kinematic Control in MIRS Subject to RCM: Novel kinematic formulations for surgical systems are derived and the movement restriction in incision point, known as RCM constraint, is resolved by active control of the system through a so-called RCM-constrained Jacobian. The proposed minimal Jacobian matrix can realize fixed/moving trocar constraint effectively in comparison with the state of the arts.
- Robot Assisted Needle Insertion using Medical Images in MIS: In this research we use KUKA iiwa robot arm for percutaneous needle insertion applications range from medical diagnosis such as biopsy to therapeutic agent delivery. This way, positioning accuracy will be increased up to 0.1 mm, the time of process will be reduced and the side effects such as injuries and dose of radiation will be decreased. Manual target Positioning is a common procedure however it is imprecise and inaccurate. According to our observations in local hospitals, the process is usually performed manually in several stages and under direct medical imaging systems such as CT-scan or ultrasound. During this intervention, usually high skills is needed in order to ensure avoidance with vital organs and precise targeting. Beside the low accuracy, the process is time consuming for patient, physician and CT-scan system. Using the robotic manipulator instead of manufacturing of a bed-mounted or patient-mounted robotic systems leads to overcome some of the design restrictions regarding to the compatibility of the size of the system with CT scan gantry, weight of the system and the material constraints which is important in artifacts avoidance and sterilization process. The new proposed workflow and control algorithms of this study can be extended to other insertion procedures and can be published as a software to correlate the robot with medical images. We can performed different scenarios (for instance needle insertion, ablation, drainage, seed implantation, reconstructive spinal surgery such as Kyphoplasty, etc.,) with the same designed set-up.
Videos:
People:
- Dr. Hamid Sadeghian, Assistant Professor, Robotics and control, University of Isfahan
- Dr. M. Saleh Jafarpisheh, Assitant Professor, Interventional Radiology, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
- Dr. Zahra Kamranian, Phd in machine vision and image processing, University of Isfahan
- Ms. Maryam Barkhordari, MSc in Biomedical Engineerig, University of Isfahan
Related Publications:
- Hamid Sadeghian, Fateme Zokaei, Shahram Hadian, “Constrained Kinematic Control in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Subject to Remote Center of Motion Constraint, ” Journal of Intelligent and Robotic systems, pp. 1-8, 2018.



- Rehabilitation Robotics: Here the aim is to develop control algorithm to exploit a robot arm for active rehabilitation of the arm- hand in stroke/SCI patients. To this end an integrated hardware/ software is designed to bring the human in the control loop. Using robots in rehabilitation have a lot of advantages. First of all it is possible to make the rehabilitation process evidence based. In other words because of recording all the motion and force data it is possible to provide effective indices as well as plots to show the progress of rehabilitation during the sessions. Moreover by using an interactive interface between the robot and the patient, the human can be brought in the control loop of the robot and thus trigger the neuroplasticity.
People:
- Dr. Hamid Sadeghian, Assistant Professor, Robotics and control, University of Isfahan, Isfahan
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wdPuaX_RAOM
https://youtu.be/owEph7jm3gE

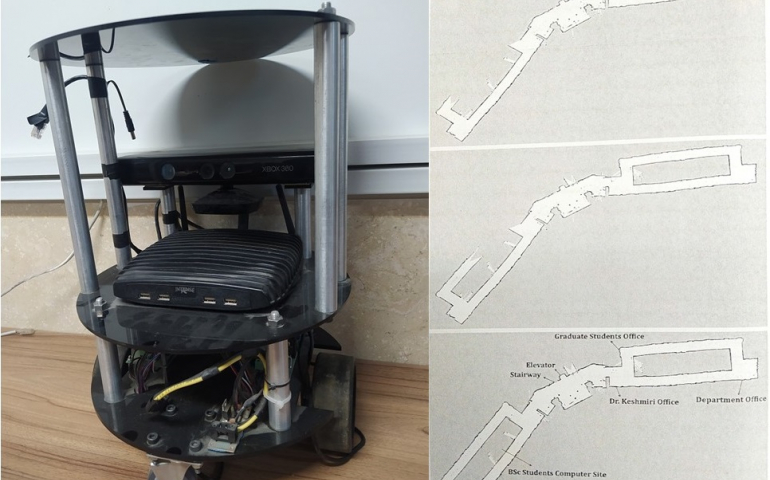
Extracting an accurate and complete map of the world is among the most difficult tasks in mobile robotics. In this regard, enabling the mobile robot to learn the map of the world and choose the optimum destination to continue the autonomous scanning of the environment, is the topic of this research. For this purpose, the Rao-Blackwellized particle filter for occupancy grid maps is used to determine the pose of the robot and create the map of the world. Furthermore, a two layered architecture is used for motion planning, considering the path planning and obstacle avoidance. The fundamental of exploration problem is determining the optimum goal among the other potential goals. The main objective of this research is to gain the ability of selecting the goal without human intervention and creating the map of the world autonomously. Hence in this work, the frontier-based exploration strategy is applied to the robot for the purpose of selecting the optimum goal. For practical implementation of the exploration problem, Robot Operating System(ROS) framework is used as the software platform of the robot. Moreover, the area of the fifth floor of the mechanical engineering department of the Isfahan university of technology is chosen as the unknown environment to test the robot. As a result, the frontier-based approach turned to be an effective algorithm for exploring the large and cluttered environments.
People:
- Mr. Majid Fattahian, MSc in Mechanical Engineerig, Isfahan University of Technology
- Dr. Mehdi Keshmiri, Professor, Robotics, Isfahan University of Technology
- Dr. Hossein Karimpour, Assistant Professor, Robotics and control, University of Isfahan
- Visual Servoing with Safe Interaction: The control of the interaction during an image based/position based visual servoing for a robot working in dynamic cluttered environments is considered. The main concerns in this scenario are the performance of the main visual servoing task, keeping the visual feature in the field of view as well as a safe physical avoidance/interaction.
- Pose Estimation using Deep Learning Approaches: A new Convolutional Neural Network is studied for the purpose of robot pose estimation. The model does not require any knowledge about the camera intrinsic parameters. New dataset is introduced and precise results are achieved via the proposed CNN model during the experiments.
Videos
People:
- Dr. Hamid Sadeghian, Assistant Professor, Engineering Department, University of Isfahan, Isfahan
- Dr. Zahra Kamranian, Postdoctorial Fellow, Computer Engineering Department, University of Isfahan, Isfahan
- Dr. Abbas Karami, Phd, Mechanical Engineering Department, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan.
Related Publications:
- Hamid Sadeghian, and Luigi Villani, “Visual Servoing with Safe Interaction”, 8th International Workshop on Human-Friendly Robotics (HFR 2015), Munich, Germany, 2015.
- Hamid Sadeghian, Luigi Villani, Zahra Kamranian, Abbas Karami, “Visual Servoing with Safe Interaction using Image Moments”, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS2015, Hamburg, Germany, 2015.
In recent years, people have become interested in interacting with a virtual world via a virtual reality system. Haptic robots are designed to provide the sense of touch in this connection. There are various and continuously increasing applications for these robots in education, medicine, entertainment, etc.
In this thesis, a new process for designing a controller is introduced, with the aim to improve the transparency of the haptic robot. Several new formulas have been obtained for calculating the controller gains, which will significantly facilitate the controller design process. In addition, a parameter study is accomplished on the effect of the haptic robot and the virtual environment parameters on the controller gains.
To have a better understanding of the system's transparency performance and comparing the results of different controllers, a new quantitative index has been introduced. The index is based on the degree of compatibility of the controlled system performance, with the desired virtual environment characteristics. The introduced transparency index shows that the proposed controller provides better transparency performance than other controller schemes.
In this research, the stability boundary of the haptic robot is investigated under various controllers. The stability boundary is plotted and the effect of the controller gains on the system stability is examined. In order to verify the new formulas, a haptic system is simulated in Simulink. Furthermore, a 1-DOF haptic robot is designed and produced. The matching between simulation results, experimental results and the results obtained from the analytical formulas shows the validity of the developed formulas.
People:
- Eng. Mehdi Shakeri, Master student, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan
- Dr. Mehdi Keshmiri, Professor, Robotics, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan
- Dr. Saeed Behbahani, Isfahan University of Technology, Isfahan